Performance Optimization Techniques in React: Memoization, useMemo, useCallback, Code Splitting, and Lazy Loading
Introduction
In this blog post, we will explore various performance optimization techniques in React that can significantly improve the performance and user experience of your applications. By understanding and applying these techniques, you can minimize unnecessary re-rendering, reduce bundle sizes, and optimize resource loading. Let's dive into memoization, useMemo, useCallback, code splitting, and lazy loading to enhance the performance of your React applications.
Memoization
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(Component);
Memoization is a technique used to cache the results of expensive computations and avoid unnecessary re-computations. In React, you can leverage the `memo` higher-order component or the `React.memo` function to memoize functional components. When a memoized component receives the same props, it skips the re-rendering process, resulting in better performance. Memoization is particularly useful when rendering large lists or when components have expensive rendering logic. By memoizing components, you can optimize performance by preventing unnecessary re-renders.
Pic Courtesy: Syncfusion
useMemo
const expensiveResult = useMemo(() => {
// Perform expensive computation here
return computeExpensiveResult(dep1, dep2);
}, [dep1, dep2]);
The `useMemo` hook in React allows you to memoize the result of a computation and avoid unnecessary re-computations. It takes a function and a dependency array as arguments. The function is executed during rendering, and the result is cached until any of the dependencies change. If the dependencies remain the same, the cached result is returned, saving computational overhead. `useMemo` is useful for calculating derived data or performing expensive calculations in a component. By using `useMemo` strategically, you can optimize your React components and improve rendering performance.

Pic Courtesy: Enlear Academy
useCallback
const handleClick = useCallback(() => {
// Handle click logic here
}, [dep1, dep2]);
The `useCallback` hook is used to memoize callback functions in React. When a component renders, functions defined within the component are re-created on each render. However, by using `useCallback`, you can memoize a function and ensure that it is not re-created unless its dependencies change. This optimization can be beneficial when passing callbacks to child components, as it prevents unnecessary re-renders of the child components. By memoizing callbacks with `useCallback`, you can improve the performance of your React application.

Pic Courtesy: Alex Devero Blog
Code Splitting
const LazyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyComponent'));
const MyComponent = () => (
<Suspense fallback={Loading...}>
<LazyComponent />
</Suspense>
);
Code splitting is a technique that allows you to divide your application's code into smaller chunks that can be loaded on-demand. By splitting your code into smaller bundles, you can reduce the initial load time of your application and improve performance. React provides different code splitting techniques such as dynamic import and React.lazy with Suspense. Dynamic import enables you to asynchronously load modules at runtime. React.lazy allows you to lazily load components, loading them only when they are needed. Suspense provides a fallback UI while the lazily loaded component is being fetched. By leveraging code splitting, you can optimize the loading performance of your React application.
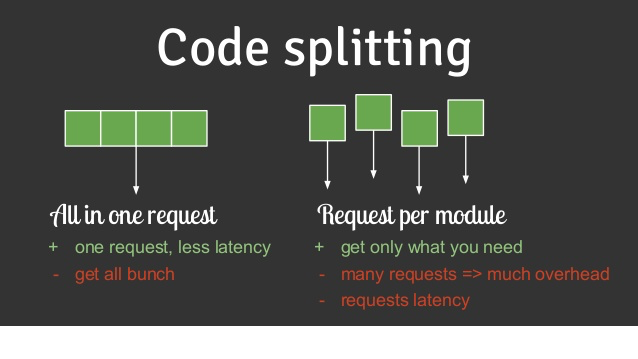
Pic Courtesy: FreeCodeCamp
Lazy Loading
const LazyImage = React.lazy(() => import('./LazyImage'));
const MyComponent = () => (
<Suspense fallback={Loading...}>
<LazyImage src="https://example.com/image.jpg" alt="Image" />
</Suspense>
);
Lazy loading is a technique that defers the loading of non-critical resources until they are actually needed. In a React application, you can use React.lazy and Suspense to lazily load components. React.lazy allows you to load components lazily, and Suspense provides a fallback UI while the component is being loaded. Lazy loading is particularly useful when dealing with large applications that contain many components. By lazy loading components or resources, you can significantly improve the initial page load time and reduce the amount of data transferred, resulting in a better user experience.

Pic Courtesy: Syncfusion
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored various performance optimization techniques in React, including memoization, useMemo, useCallback, code splitting, and lazy loading. By applying these techniques, you can optimize the rendering process, reduce bundle sizes, and enhance the loading performance of your React applications. Consider the specific requirements of your application and choose the appropriate optimization techniques to improve the overall performance and user experience.
A good read overall
ReplyDeleteEvery topic has been explained clearly with relevant implementations.
ReplyDelete